Monopole Antenna Project
There is document - Monopole Antenna Project available here for reading and downloading. Use the download button below or simple online reader.
The file extension - PDF and ranks to the Documents category.
Tags
Related
Comments
Log in to leave a message!
Description
MONOPOLE ANTENNA 2007 Page [2] Monopole Antenna Analysis, Design and Simulation using Computer Supervisor: DrOmer Al Saraereh Students: Abdul Karem AAl Sbeeh Aiman SResiq Ahmad HZaid Ibrahim MHruob Mohammed Hisham Ismail Abdel Razzaq Yazeed Sulaiman Jaafar HAbuRaad Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Hashemite University 2007 Hashemite University | Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering MONOPOLE ANTENNA Page [3] Introduction Chapter I Over view about mo
Transcripts
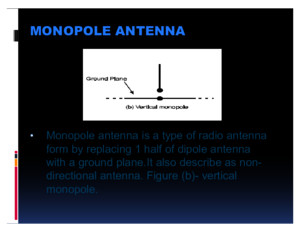
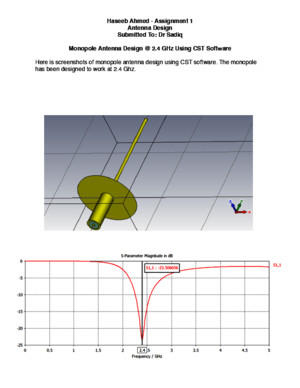
MONOPOLEANTENNA Page[2] HashemiteUniversity|DepartmentofElectricalandComputerEngineering MonopoleAntenna Analysis,DesignandSimulationusingComputer Supervisor: DrOmerAlSaraereh Students: AbdulKaremAAlSbeehAimanSResiqAhmadHZaidIbrahimMHruobMohammedHishamIsmailAbdelRazzaqYazeedSulaimanJaafarHAbuRaad 2007 DepartmentofElectricalandComputerEngineeringHashemiteUniversity2007 MONOPOLEANTENNA Page[3] HashemiteUniversity|DepartmentofElectricalandComputerEngineering Fig1 :MonopoleAntenna Introduction ChapterI OverviewaboutmonopoleAntenna Nowdays,wirelesscommunicationsystemsarebecomingincreasinglypopularHowever,thetechnologiesforwirelesscommunicationstillneedtobeimprovedfurthertosatisfythehigherresolutionanddataraterequirementsInthecommunicationsystemthemorethingsislooktoisthecoastandlowpowerdeviceanditisthemonopolewhichpreviousthingisusedandstillbeimproveforthecommunicationsystemMonopoleisatypeoftheradioantennaformedbyreplacingonehalfofadipoleantennawithagroundplaneatrightanglestotheremaininghalfIfthegroundplaneislargeenough,themonopolebehavesexactlylikeadipole,asifitsreflectioninthegroundplaneformedthemissinghalfofthedipoleThisstudyisrestrictedtoamonopolegeometryconsistingofaverticalcylindricalelementatthecenterofaperfectlyconducting,infinitelythin,circulargroundplaneinfreespaceThisgeometryisofinterestbecauseitsradiationpatternisuniformintheazimuthdirectionandbecauseitselectricalcharacteristicsareprimarilyafunctionofonlythreeparameters,namely,theelementlength,theelementradius,andthegroundplaneradius,wheneachisnormalizedtotheexcitationwavelengthTherefore,thisgeometryisconducivetoanalysis,experimentalverification,andstandardizationAtypicalfeedforthemonopoleantennaisacoaxiallinewithitsinnerconductorconnectedthroughaholeinthegroundplanetotheverticalmonopoleelementanditsouterconductorconnectedbymeansofaflangetothegroundplaneTypically,theinnerconductor’sdiameterisequaltothemonopoleelement’sdiameterandtheouterconductor’sdiameterisequaltothegroundplaneholediameterUnlessstatedotherwise,suchafeedwillbeassumedinthisstudyTheratioofthecoaxialline’soutertoinnerconductordiametersaffectstheantenna’sinputimpedance,butonlysignificantlyforarelativelythickmonopoleelementonaverysmallgroundplaneFortheidealizedcaseofagroundplaneofinfiniteextentandinfiniteconductivity,themonopoleantennamaybemodeledbythemethodofimagesasadipolewithonehalftheinputimpedanceanddoublethepeakdirectivityofthedipoleTheinfinitegroundplanepreventsmonopoleradiationintothehemispherebelowthegroundplane,butallowsaradiationpatternidenticaltothatofthedipoleintheupper MONOPOLEANTENNA Page[4] HashemiteUniversity|DepartmentofElectricalandComputerEngineering Fig2 :MonopoleBroadcasting hemisphereHowever,foramonopoleelementmountedonagroundplaneoffiniteextent,theouteredgeofthegroundplanediffractsincidentradiationinalldirections,andconsequentlymodifiesthecurrentsonthegroundplaneandtheverticalelementfromthoseofaninfinitegroundplaneAttheouteredgeofthegroundplane,thecurrentsonitstopandbottomfacesareequalinmagnitudebutoppositeindirectionbecausethenetcurrentmustbezeroattheedgeOuteredgediffractionbecomesincreasinglysignificantwithdecreasingsizeofthegroundplanebecauseoftheincreasingmagnitudeofthecurrentsonthegroundplanefacesattheouteredgeEdgediffractioncanaltertheinputimpedancebymorethan3dBanddirectivityintheplaneofthegroundplanebymorethan6dBfromthevaluesforagroundplaneofinfiniteextentTheoreticalmodelsexistforpredictingtheeffectsofdiffractionbytheouteredgeofthegroundplaneTheexistingmodelsmaybeclassifiedintotwocategories,distinguishedbywhetherthecurrentdistributiononthemonopoleelementisinitiallyknownorunknownWhenthemonopoleelementisverythinandnottoolong,itscurrentdistributionisapproximatelysinusoidalandindependentoftheradiusofthegroundplaneConsequently,theelement’scurrentdistributioncanbeinitiallyspecifiedandwendedonlydeterminethegroundplane’scurrentdistributionForthiscategoryofmonopoles,thetheoreticalmodelsreportedintheliteratureessentiallyconsistofBardeen’sintegralequationmethodforagroundplaneradiusthatissmallcomparedtoawavelength[1],Richmond’smethodofmoments(groundplaneonly)foragroundplaneradiusthatisnottoolargecomparedtoawavelength[2],LeitnerandSpence’smethodofoblatesphericalwavefunctionsforagroundplaneradiusthatiscomparabletoawavelength[3–5],Tang’sscalartheoryofdiffractionandthegeometrictheoryofdiffraction(GTD)foragroundplaneradiusthatislargecomparedtoawavelength,andStorer’svariationmethodforagroundplaneradiusthatisverylargecomparedtoawavelength[3]Whenthemonopoleelementisrelativelythick,itscurrentdistributionisnolongersinusoidal,andthecurrentdistributiononboththemonopoleelementandthegroundplaneconsequentlyneedtobedeterminedasafunctionofthegroundplaneradiusForthiscategoryofmonopoles,thetheoreticalmodelsreportedintheliteratureessentiallyconsistofRichmond’smethodofmomentsforgroundplaneradiusthatisnottoolargecomparedtoawavelength[4]andAwadallaMaclean’smethodofmoments(monopoleelementonly)combinedwiththegeometrictheoryofdiffractionforgroundplaneradiusthatislargeorcomparabletoawavelength[9,10]ThieleandNewhousehavealsoreportedamodelthatcombinesthemethodofmomentswiththegeometrictheoryofdiffraction,buttheircomputerprogramisunavailable Applicationsofmonopoleantenna MonopoleantennasarecommonlyemployedinairborneandgroundbasedcommunicationsystemsatawiderangeoffrequenciesTheelectricalpropertiesofsuchantennasaredependentuponthegeometryofboththemonopoleelementandthegroundplaneTypically,themonopoleelementmaybeelectricallyshort(lengthismuchlessthanaquarterwavelength)ornearresonant(lengthapproximatelyaquarterwavelength),anditmaybethin(lengthtoradiusratioismuchgreaterthan104)orrelativelythick(lengthtoradiusratioof101to104)Inaddition,thegroundplanedimensionsmayvaryfroma
Recommended